Date: 9-10:30 AM SGT, September 10th 2024 / 9-10:30 PM EST, September 9th 2024
Session Title: The Power of Parallel EVM Execution to Transform Blockchain Performance
NTU I&E x HackQuest MOOC is free and open to all individuals interested in Web3. The MOOC is led by top voices in crypto including Yat Siu (Co-founder, Animoca), Ed Felten (Co-founder, Offchain Labs), Sergey Gorbunov (Co-founder, Axelar), Scott Moore (Co-founder, Gitcoin), Haider Rafique (CMO, OKX), Austin Griffith (Developer Onboarding, Ethereum Foundation), Anna Yuan (Stablecoins Lead, Solana Foundation), and many more. For those who prefer having a text summary and review material, this study note provides a recap of what’s covered during the MOOC. Happy learning!
Main Topic: Scaling Ethereum with Parallel Execution of the EVM
Objectives:
1.Understand the architecture and workflow of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
2.Analyze the limitations of the sequential EVM and the benefits of parallel execution.
3.Explore the Block-STM method and Reddio’s approach to enhancing EVM performance.
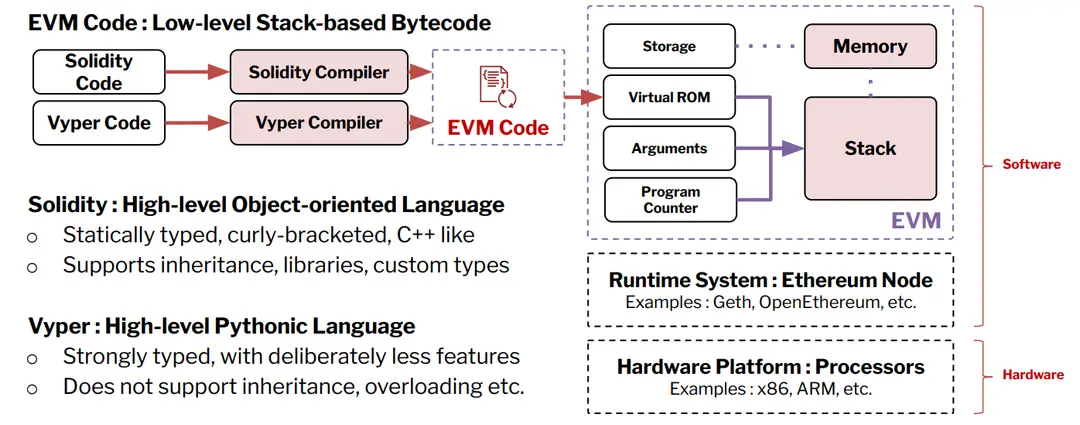
Section 1: Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
●Definition:
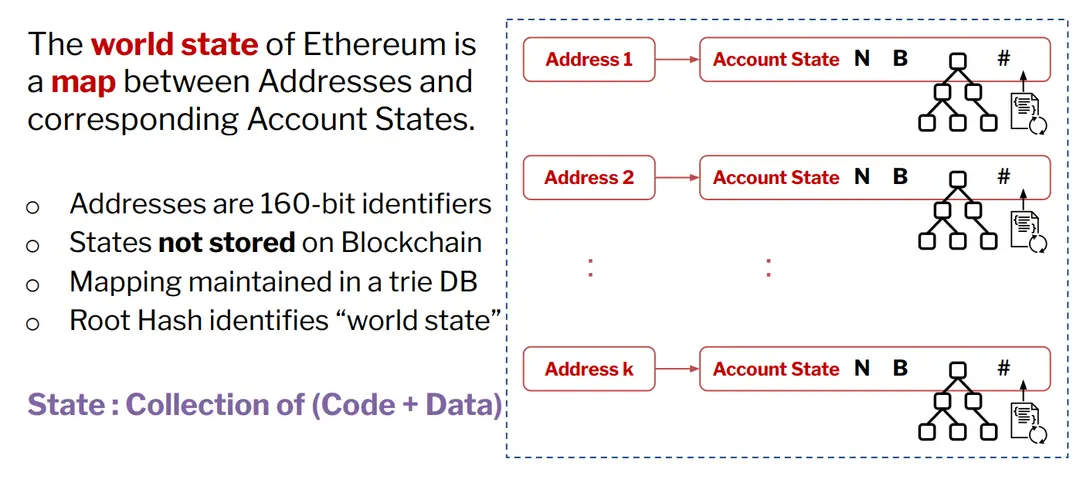
●The EVM is the runtime environment for executing smart contracts on Ethereum, functioning as a decentralized, stack-based virtual machine that processes transactions and manages state updates. ●Structure:
●The Ethereum world state maps addresses to account states, stored in a trie database. Each account's state consists of code (smart contracts) and data, ensuring a consistent record of interactions.
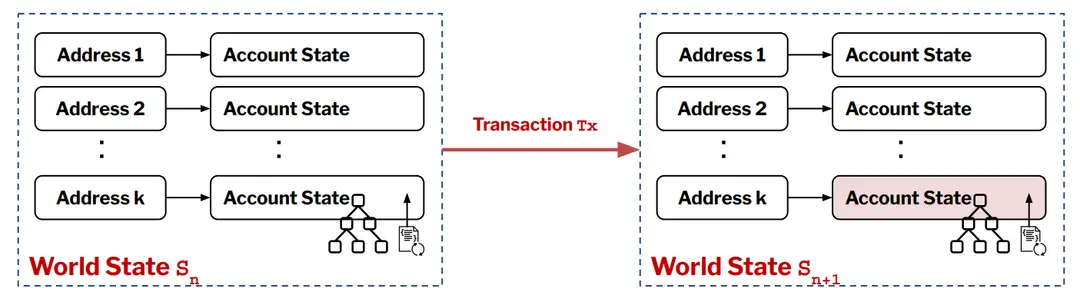
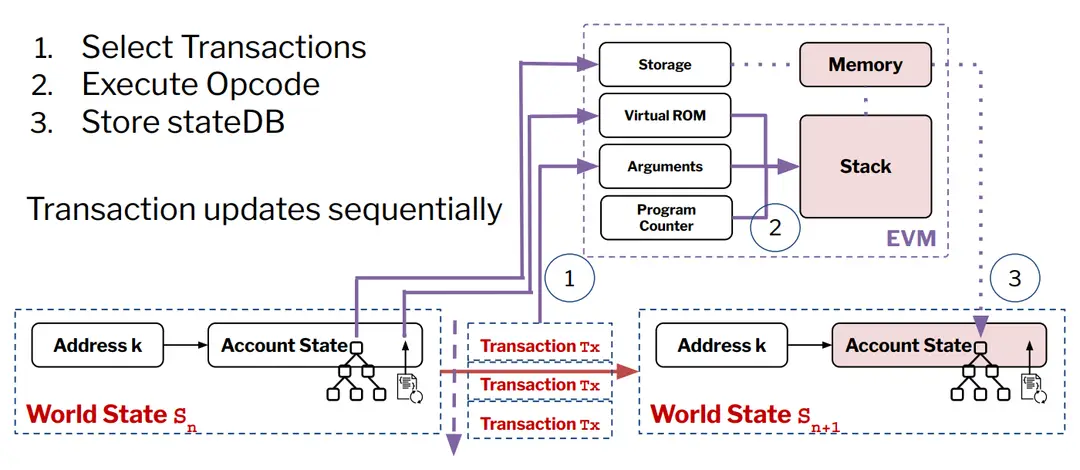
1.3 State Transition Mechanism
●Process:
●The EVM operates on a state transition model initiated from a genesis state. Each transaction updates the world state, transitioning it to the next state based on executed operations, allowing for atomic updates across accounts.
Section 2: EVM Architecture
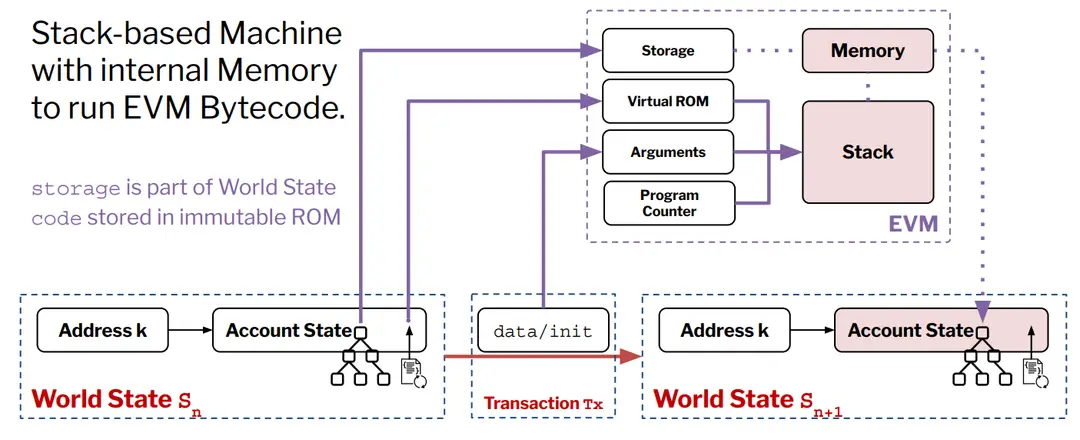
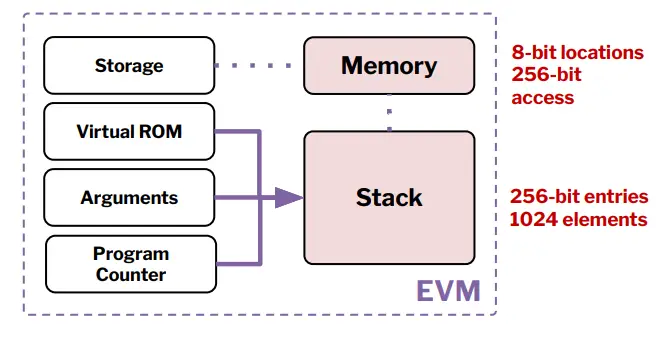
●Key Components:
●Stack: Holds intermediate values for calculations.
●Memory: Temporary storage for data during execution.
●Storage: Persistent storage for account states, integral to the world state.
●Program Counter: Tracks the execution position in bytecode.
●Opcode Functionality:
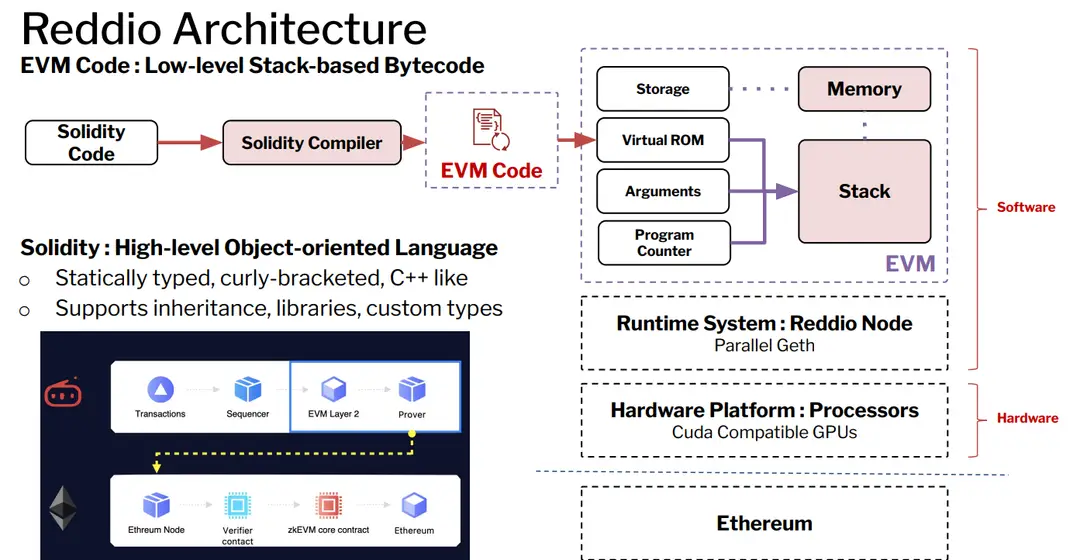
●The EVM supports various operations, including arithmetic and logic, through low-level stack-based bytecode. This enables Turing-complete execution of smart contracts, facilitating diverse applications.
●High-Level Languages:
●Smart contracts are typically written in languages like Solidity and Vyper, which are compiled into low-level EVM bytecode for execution, allowing developers to leverage high-level programming constructs.
Section 3: Limitations of the Sequential EVM
3.1 Workflow of the Sequential EVM
●Transaction Processing:
●The sequential EVM processes transactions one at a time:
1.Select transactions from the mempool. 2.Execute corresponding opcodes.
3.Update the state in the state database.
●Performance Issues:
●The sequential processing leads to slow transaction speeds and inefficiencies, particularly during network congestion, limiting the scalability of decentralized applications (dApps).
Section 4: Parallel Execution of the EVM
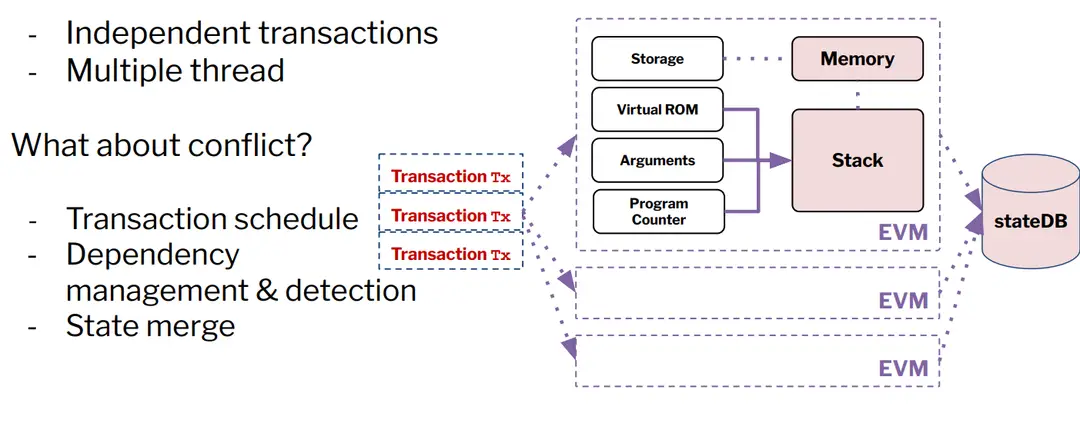
4.1 Introduction to Parallel Execution
●Independent Transactions:
●Parallel execution enables multiple transactions to be processed simultaneously, significantly enhancing throughput and scalability by reducing bottlenecks.
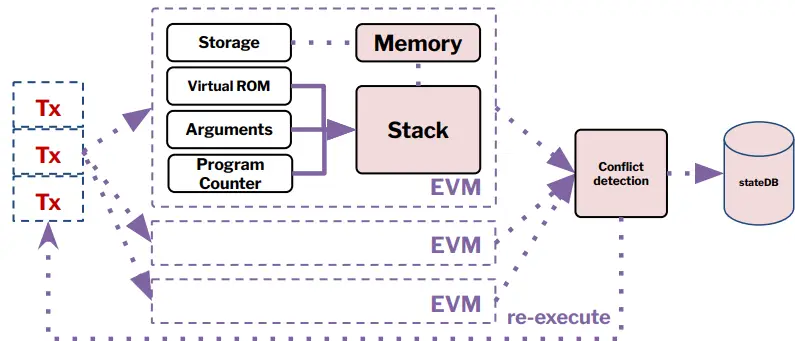
●Optimistic Parallelization:
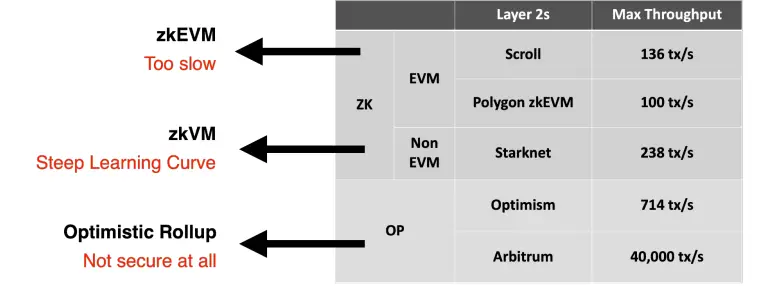
●The Block-STM (Software Transactional Memory) method promotes optimistic parallel execution with dynamic conflict detection, enabling more efficient handling of transactions across multiple chains.
4.3 Advantages of Parallel Execution
●Scalability:
●Parallel execution allows for increased performance of dApps in various domains, such as decentralized exchanges (DEXs), GameFi, low-latency applications, and microtransactions.
Section 5: Reddio’s Approach to EVM Scaling
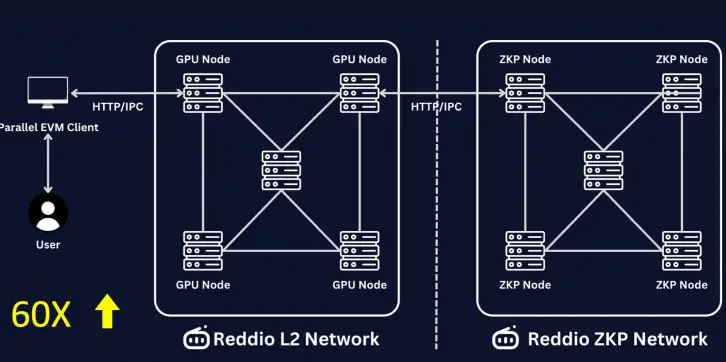
●GPU Acceleration:
●Reddio leverages decentralized GPU networks to enhance processing capabilities, enabling more efficient transaction handling and scaling, which is critical for meeting user demands.
5.2 Architecture Overview
●Reddio Node:
●The architecture integrates GPU acceleration with a modular sequencer SDK, allowing for efficient transaction processing while maintaining compatibility with existing Ethereum smart contracts.
Parallel execution of the EVM offers a promising solution for scaling Ethereum, addressing the limitations of sequential processing. The Block-STM method provides a robust framework for optimistic parallelization, facilitating efficient transaction handling. Reddio’s architecture utilizes GPU acceleration to maximize performance, establishing a new standard for scalability in the Ethereum ecosystem.
1.Q1: How do you see the future of ETH compared to Bitcoin?
Answer: Thank you for the question. While I'm not giving investment advice, I believe that Ethereum's innovative capacity has always driven the market forward. The token economics for both Ethereum and Bitcoin are designed with different goals in mind, and I see this as a key factor for their future valuations.
2.Q2: What's your perspective on the Indian developer ecosystem?
Answer: I have had positive experiences with Indian developers in previous roles, and I see a robust market for both web2 and web3 innovations coming from India. The talent pool is eager to learn and apply new technologies, making it an exciting space to watch.
3.Q3: How would you explain concepts like ZK and ZKVM to newcomers?
Answer: For newcomers, I would simplify these concepts by relating them to everyday technology. For instance, ZK can be likened to a secure compression algorithm that ensures data integrity, while the concept of layer two can be explained through familiar payment wallets that improve transaction speed and efficiency.